Design Template by Anonymous
Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process is a five-step, non-linear design process that many user-centered designers base their designs around. This process is popular with UX designers, UI designers, and product management teams in various situations. This process is iterative, which means it can repeat certain steps as needed. This allows design teams to get their design as close to how the users like it as possible.
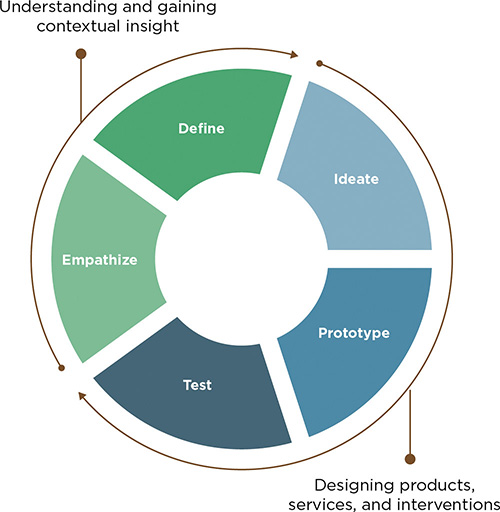
Step 1: Emphasize
During this phase, the design team will emphasize with the target audience. First, the design team researches the target audience and takes notes about them. The team should get as deep of an understanding as possible of the target audience and the problem they're trying to solve since the goal of user-related design is to fill the gap between the users and the solution to their problem through the design.
Empathy
During the emphasizing step of the design thinking process, the design team will learn how to view the problem from the target audience's perspective. This is known as empathy. Empathy is a critical value for a web designer, or any designer, to have because it helps the designers see the problems from the perspective of the users. Empathy is defined as seeing the audience's world, appreciating them as people, understanding how they feel about their situations, and communicating the understandings of the team with them.
Step 2: Define
By the time the design team enters the second step, which is to define the problem, they should have a sense of empathy for the target audience and understand their world and the problem they're trying to solve. Having a sense of empathy makes the problem much easier to solve since it tells the design team the user's perspective of the problem. The design team should also have substantial knowledge about the problem they're trying to solve and know instinctively what needs to be addressed. To address it, the design team will work together to develop a problem statement they can use throughout the duration of the project.
Problem statements
A problem statement is a written statement of the problem the design team is working to solve. In the case of web design, the problem statement should be written from the perspective of the users. It is not about the company or stakeholder's personal goals, but is instead about the target audience's issue. The team should state why the problem matters and provide proof of its effects so the rest of the team takes action, especially after seeing a visual representation of the problem.
Step 3: Ideate
At this point, the design team should have an effective problem statement and should be ready to ideate solutions. The team should have a clear understanding of the problems and the users' needs. It is important that team members do not limit their ideas because often, the most random ideas can be groundbreaking ideas. Innovation is only possible when several new ideas are shared, and innovation is what leads to success with a user-centered design.
Ways to ideate:
There are several ways to ideate solutions. The most common methods people use are brainstorming, brainwriting, the “worst possible idea” method, and the “SCAMPER” method. In the beginning of this step, the brainstorming and “worst possible idea” methods tend to be the most popular.
“Worst possible idea” method:
- The “worst possible idea” method is an ideation method where designers bring up the worst ideas possible to avoid looking silly in front of everyone. This is a method people use to explain why the ideas are bad, and how other ideas are better. However, sometimes these “worst possible ideas” can come out as good ideas among other team members.
SCAMPER
- Substitute
- Change random elements to improve the design.
- Combine
- See what features can be combined to make the solution more innovative.
- Adapt
- Add certain features to match the circumstances of the users and their problems.
- Modify
- Change different visual and behavioral aspects to provide a better user experience.
- Put (to another use)
- See how the design could be put to other uses. Designs with multiple uses tend to be more successful.
- Eliminate
- Remove unnecessary or annoying elements that users would be better off without.
- Reverse
- Go back to any steps as needed.
Step 4: Prototyping
A prototype is an early model that looks, behaves, and responds like the finalized product. Prototyping is the process of creating prototypes and iterating them repeatedly. These prototypes should be tested within the team, who should give feedback on the prototypes to improve them. The goal of prototyping is to find the best solution possible for solving the problem statement defined in step 2. Prototypes get accepted, rejected, and improved based on how the users experience them. As they fail, the designers should take note of where they didn't work so they know to avoid these approaches. Prototyping earlier in the design thinking process can save the company a lot of time and money.
Step 5: Test
The last step of the design thinking process is to test the product rigourously. Test with users for about 15-20 minutes each, and if they report a problem with the design, the design team should go back to ideating and find ways to change it for the next set of prototypes. Good user testing helps the design team further understand the target audience and builds a deeper sense of empathy towards them. The designers should take note of how the users feel about the product and their behaviors and thoughts towards it. The designers should get as deep of an understanding as possible during this step, similar to step 1. After this step, the design team should go back to any previous steps necessary until the product fixes the users' problems.

The Design Thinking Process is Non-Linear
Because the design thinking process is non-linear, the design team can take multiple different approaches to different steps. Some team members might focus more on the user research and defining the problem, others might focus on prototyping, and more might focus on user testing. This allows the team to concentrate on different aspects of the process without worrying about the next. For instance, new prototypes could easily be created after user testing because another team member might have a better idea. The goal of the design thinking process is to focus on the relationship between the design team and the target audience for whom they're solving the problem for.