Design Template by Anonymous
Fundamentals of Color Theory
Understanding Color Theory
Understanding how color works and how it can be applied is essential for creating smart and effective designs in any professional setting. Color theory is known for implementing various guidelines and rulesets about color for designers to follow. It utilizes color psychology, color associations, and the human perception to help create strong, well-rounded designs with better readability, usability, and aesthetic.
The Color Wheel
The color wheel is a great tool for understanding the fundamentals of color theory through providing a visualization of the different relationships found in colors.
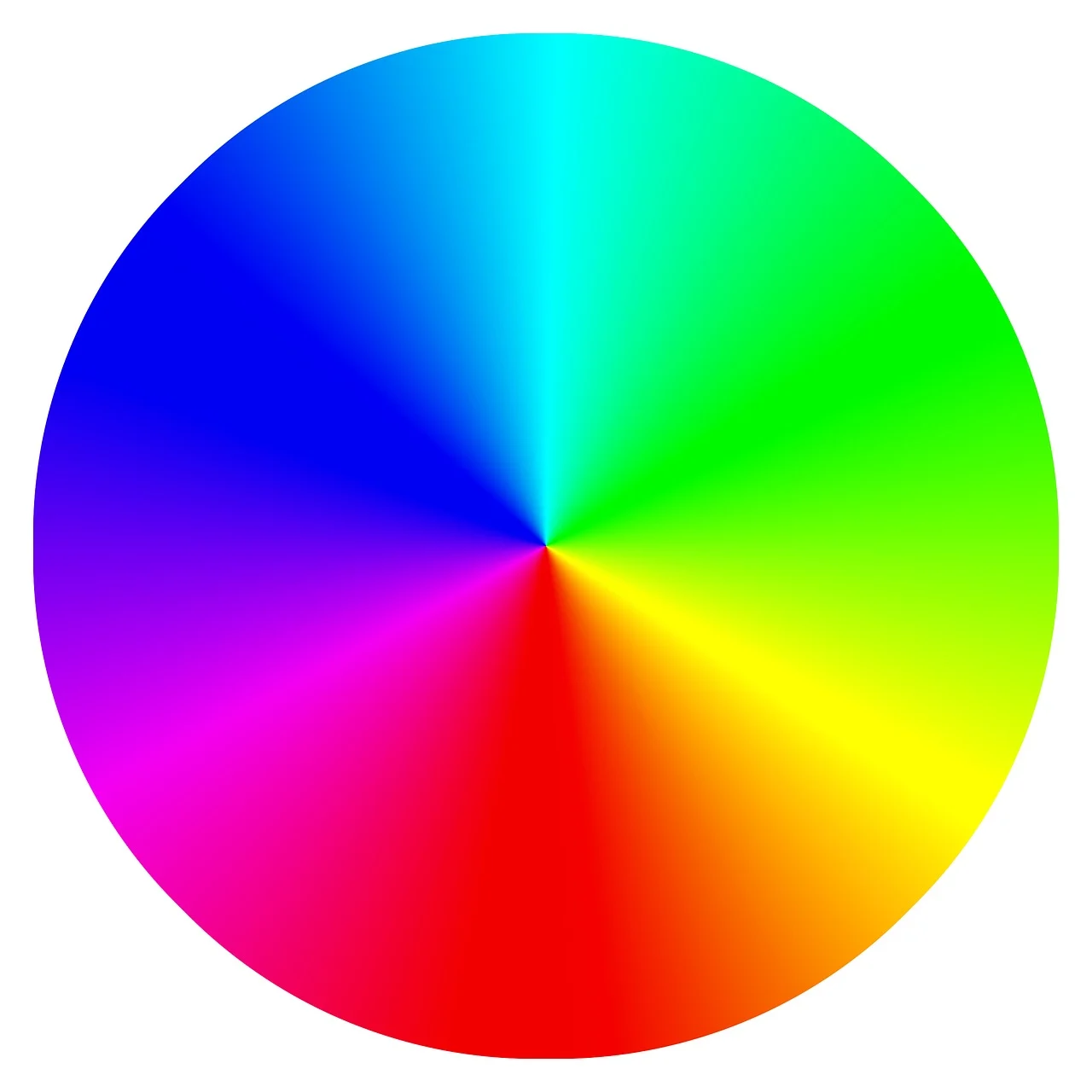
Hue
A Hue refers to a color on the visible spectrum within the color wheel. This includes red, orange, yellow, green, indigo, and violet (indigo and violet are typically replaced with purple on color wheel for simplification). Within these hues consists of the primaries, secondaries, and tertiaries.
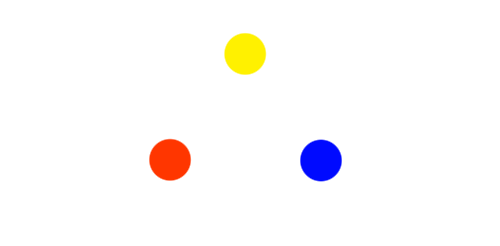
Primary
Primary colors typically refer to colors that can’t be created by combining with other colors. They consist of red, yellow and blue.
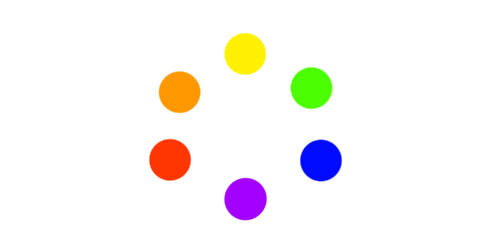
Secondary
Secondary colors, unlike primary, consist of combining or mixing the primary colors to create new colors. Where green is from a combination of blue and yellow, orange is from red and blue, and purple is from blue and red.
Tertiary
Tertiaries are a combination of one primary and one secondary color. For example yellow and green makes yellow-green, blue and purple makes blue-purple, and red combined with orange makes red-orange.

Lightness
Hues also have varying degrees of lightness and darkness which is known as its light intensity. Yellow is the lightest hue and purple or blue is typically the darkest.
Tints
Tints are essentially any hue that is combined with white. These can be pastels or even certain off-whites such as cool or warm whites (whites with a hint of blue or orange)

Tones
Tones are any hue that is combined with grey. They tend to have a dulling effect on hues, which makes up a range of colors known as neutrals, with popular examples including beige and grey-brown.

Shades
Shades are any hue that includes black. Typically used to depict shadows and has an effect of making light colors lighter.
