Design Template by Anonymous
Introduction
What is HCI?
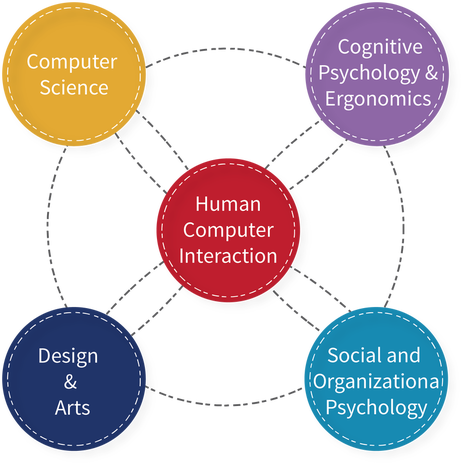
Human-Computer Interaction, or HCI, is a philosophy, field of practice, and methodology for design. Its aim is to make humans interacting with technology to be a more enjoyable experience. There are many fields encompassed within HCI: psychology, to understand how the brain interacts with machines or other things; graphic design or other visual media, to ensure the design aids the user; ergonomics, to determine how to physically design things; and sociology, to have a better understanding of how humans behave. Each of these areas of study contributes to what makes HCI effective, which is to make the experience while using technology, products, or devices more sensible to the user, and consistent with how humans behave. HCI is a field that is the umbrella of many other aspects of usability design. Within web design, this encompasses accessibility, user experience, user interface, and graphic design.

In the image above, a man is flipping through graph options, which is also seen on the large computer on the desk in front of him. Nowadays, making a graph is much easier than what he's doing! This is just one small example of how humans interacting with computers has changed over time.
Basic Principles
The basic principles of HCI are used for any good usable design, which is not just limited to computers. According to Don Norman, an author that established many ideologies of HCI in writing, named the concepts as:
- Affordances
- Signifiers
- Constraints
- Mapping
- Feedback
This will be expanded upon later in this tutorial.
Applications
There are many applications for HCI. This tutorial focuses on Web applications, but other fields also use HCI, like engineering for machinery, product design for any physical object, and many others. Think of the design of a door handle; if it is not clear which way to turn it, the user will be confused as to how to leave or enter the room from which they came. Similar to how web design works, limiting how much the user has to think about what to do is the goal of good design. It should be intuitive or solve a problem that previous forms of the same object failed to do.